# Carrier Sense Multiple Access Collision Detection (CSMA/CD)
Rather than independently making a decision:
- Carrier sensing (listen before speaking): node listens to the channel before transmitting and waits until it is quiet before transmission
- Collision detection (stop talking if someone else begins talking): node listens to the channel while transmitting and stops if there is interference.

# Taking turns
Each node take turns to transmit some data.
- Polling: a master node polls each node in a round robin fashion to tell them when and how much they can transmit.
- Token passing: each node passes a token to another in a fixed order.
# The gory details
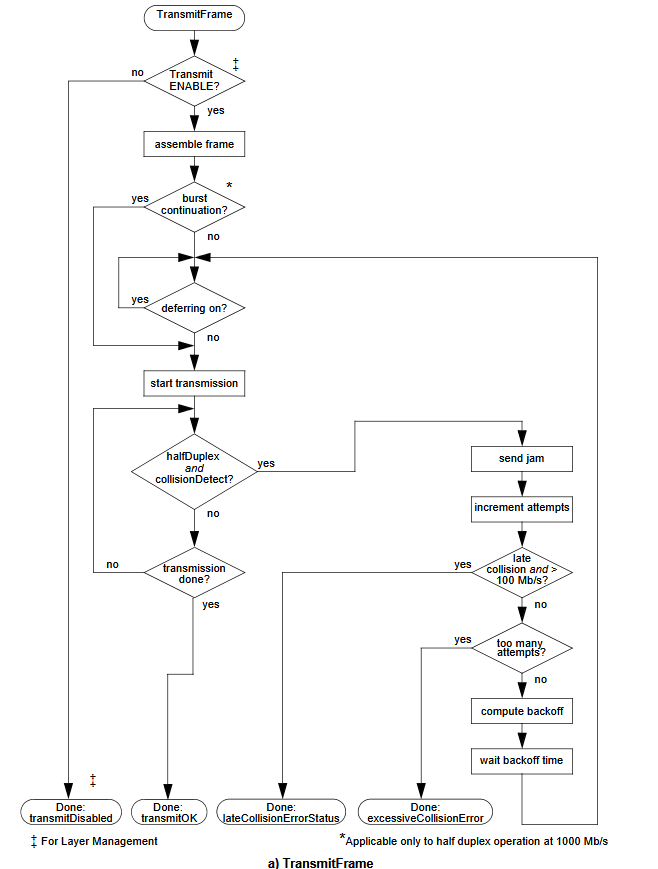
# Deference
When a packet is submitted by the MAC client for transmission, the transmission is initiated as soon as possible with some rules: Half duplex mode
- Even when it has nothing to transmit, the CSMA/CD MAC sublayer monitors the physical medium for traffic by watching the carrierSense signal provided by the PLS. Whenever the medium is busy, the CSMA/CD MAC defers to the passing packet by delaying any pending transmission of its own.
- After the last bit of the passing packet (that is, when carrierSense changes from true to false), the CSMA/CD MAC continues to defer for a proper interPacketGap (see 4.2.3.2.2). If, at the end of the interPacketGap, a packet is waiting to be transmitted, transmission is initiated independent of the value of carrierSense. When transmission has completed (or immediately, if there was nothing to transmit) the CSMA/CD MAC sublayer resumes its original monitoring of carrier- Sense.
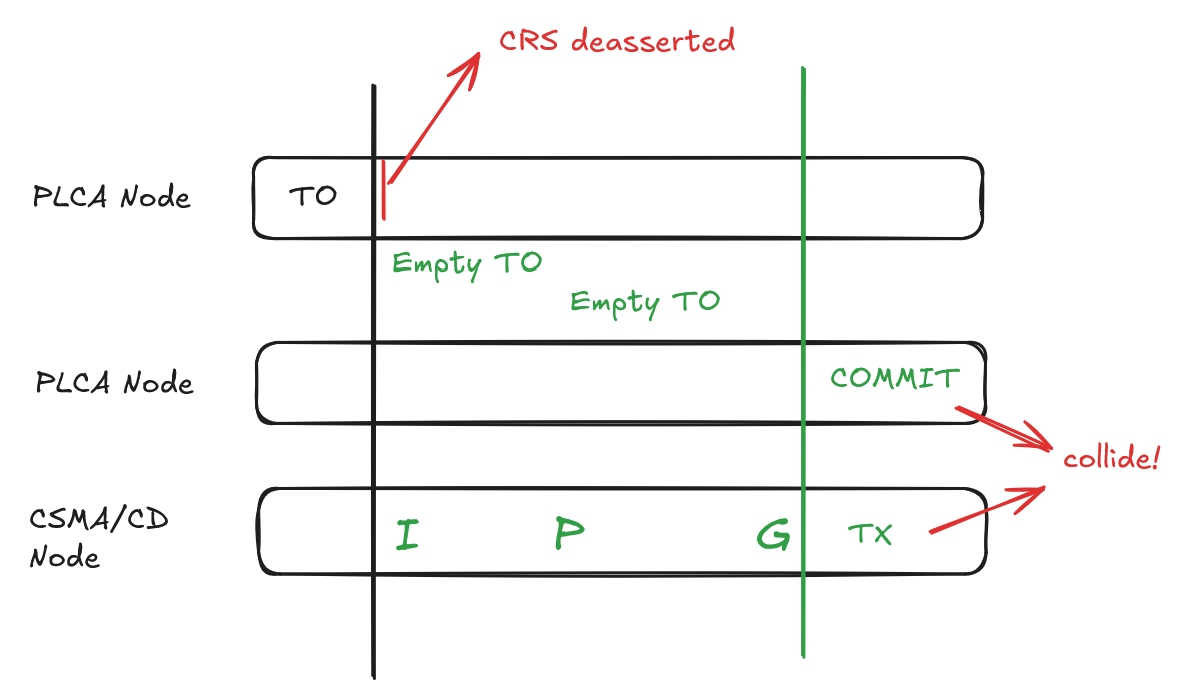
This can cause collisions with
PLCA nodes in such a manner: